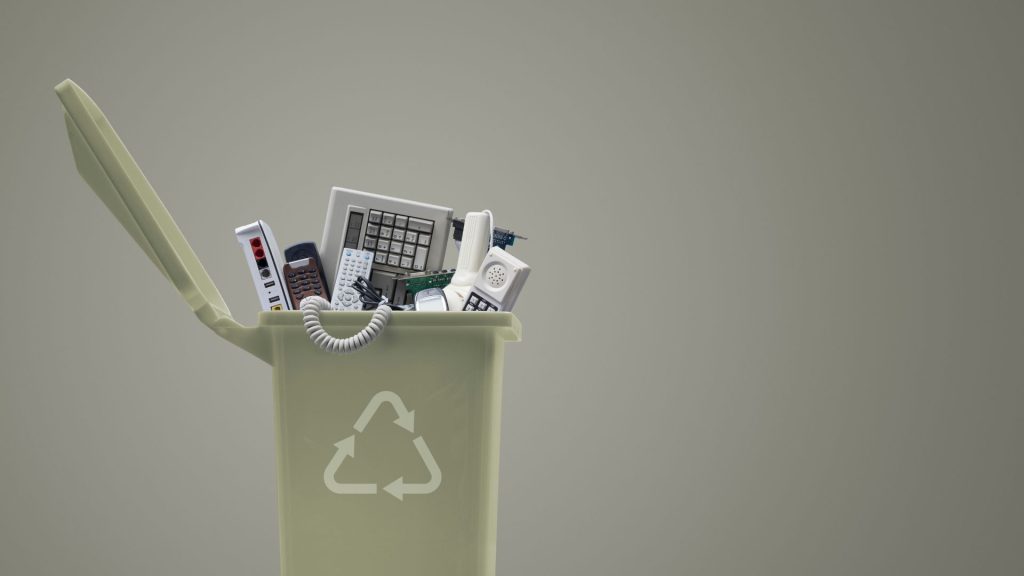
Electronic waste, or e-waste, includes a variety of discarded devices that can contain hazardous substances such as lead, mercury, and cadmium. These materials, when improperly handled, pose serious risks to both human health and the environment. Exposure to toxic chemicals can result from simple contact or inhalation, and contamination of soil and water sources is a frequent consequence of careless disposal. It’s crucial to recognize which items fall under the category of hazardous e-waste, including old computers, batteries, monitors, and other electronic devices. Understanding the risks involved lays the groundwork for responsible disposal practices, ensuring the safety of your household and your community. Additionally, separating hazardous e-waste from regular trash helps streamline the recycling process, making it more efficient and safer for professionals who handle these materials daily.
Disposing of hazardous e-waste requires careful planning and attention to detail. Simply tossing electronics into the garbage is no longer an acceptable practice due to regulations and environmental concerns. Implementing a strategy that involves collection, secure storage, and proper handoff to certified recycling centers significantly reduces potential harm. Educating yourself about local disposal regulations and available recycling programs equips you with the knowledge to make environmentally conscious choices. By taking these steps, you not only protect your immediate surroundings but also contribute to broader efforts aimed at preserving natural resources and minimizing landfill waste. Proper understanding of hazardous e-waste lays the foundation for a safer, greener future.
Identifying Hazardous Components in Electronics
Certain components in electronic devices are particularly hazardous and require careful handling. Batteries, especially lithium-ion or lead-acid types, are highly reactive and can explode or leak harmful chemicals if damaged. Circuit boards often contain traces of heavy metals, which can be toxic if released into the environment. Cathode ray tube monitors and older LCD screens contain significant amounts of lead, while fluorescent lighting used in some devices may harbor mercury. Recognizing these components before disposal is essential to avoid accidents and ensure they are processed safely by professionals. Labeling items with potential hazards and segregating them from non-toxic electronics can also help waste management services handle them appropriately.
Hazardous components are not always obvious to the untrained eye, making awareness and education crucial. Manufacturers and recycling centers often provide guidelines for identifying dangerous elements in devices, which can guide your disposal strategy. Using protective equipment such as gloves and eye protection when handling these items reduces personal risk. Moreover, storing hazardous e-waste in secure, moisture-free containers prevents chemical leaks and minimizes environmental contamination. By thoroughly identifying the risky components and understanding their properties, individuals can play a vital role in preventing ecological damage and safeguarding public health, reinforcing a culture of responsible e-waste management.
Preparing E-Waste for Safe Disposal
Before turning over electronic waste to a recycling facility, preparation is key to ensure safety and compliance with environmental standards. Begin by backing up data from devices such as computers, smartphones, and external drives to prevent loss of valuable information. Once data is secured, remove batteries and other hazardous parts and store them separately in a safe, labeled container. This step is critical in preventing accidental chemical exposure or reactions during transportation. Additionally, check with local disposal programs for specific instructions, as regulations can vary between municipalities and counties, affecting how e-waste must be handled.
Proper preparation also includes cleaning and organizing the materials for easier processing. Removing cables, accessories, and peripheral parts not only makes recycling more efficient but also reduces the risk of damage to equipment and exposure to toxins. When packaging items, use boxes or containers that prevent breakage and potential spills of hazardous substances. This careful organization ensures that e-waste reaches certified recycling facilities intact and ready for processing, minimizing the environmental footprint. Thoughtful preparation is a proactive measure that makes the disposal process smoother and safer for everyone involved.
Using Certified E-Waste Recycling Facilities
Certified e-waste recycling facilities are equipped to handle hazardous materials safely, ensuring they are processed in an environmentally responsible manner. These facilities follow strict guidelines to separate, decontaminate, and recycle electronic components, recovering valuable metals while preventing toxic substances from entering landfills. Utilizing certified centers is vital for compliance with local laws and environmental regulations. Look for recycling centers with industry-recognized certifications that guarantee adherence to safety and sustainability standards, which provide peace of mind when disposing of complex electronics.

Professional facilities also offer convenient services such as pickup and secure data destruction, addressing both safety and privacy concerns. By choosing a certified recycler, you reduce the risk of hazardous substances leaching into the environment and support a circular economy where materials are reused rather than discarded. Engaging with reputable e-waste recyclers promotes responsible disposal habits and fosters community awareness about the importance of keeping electronics out of landfills. Certified facilities serve as a critical link in the chain of sustainable electronic waste management.
Safe Transportation of Hazardous E-Waste
Transporting hazardous e-waste requires careful attention to prevent accidents and environmental contamination. Proper packaging is essential, with leak-proof containers for batteries and padding for fragile items such as screens. Avoid mixing e-waste with general household trash, as accidental breakage can release toxic chemicals. During transport, keep items upright and secure to minimize movement that could damage components. Additionally, follow all local regulations regarding the transport of hazardous materials, including labeling and quantity restrictions.
When transporting e-waste yourself, ensure your vehicle is ventilated and avoid storing materials in hot or humid conditions, which can exacerbate chemical reactions. For larger quantities or particularly dangerous items, professional services offer safer alternatives, handling pickup and transportation with specialized equipment. This reduces personal risk and ensures compliance with environmental laws. Safe transportation is a critical stage in the disposal process, protecting both the individual and the community while ensuring that hazardous e-waste reaches recycling centers intact and ready for responsible processing.
Minimizing Environmental Impact Through Recycling
Recycling hazardous e-waste mitigates its negative environmental impact by preventing the release of toxic chemicals into ecosystems. Metals, plastics, and glass components can be recovered and reused, reducing the need for raw material extraction and lowering energy consumption. Responsible recycling also curtails the buildup of waste in landfills, protecting soil and water quality and preserving biodiversity. By contributing e-waste to certified recyclers, individuals actively participate in a sustainable system that prioritizes conservation and public health.
Furthermore, recycling programs help raise awareness of the ecological consequences of improper disposal. Educational campaigns, community collection events, and corporate recycling initiatives demonstrate the collective benefits of proper e-waste management. The recovery of valuable materials not only has economic advantages but also encourages innovation in sustainable product design. Embracing recycling as part of hazardous e-waste disposal fosters an environmentally conscious mindset that extends beyond the disposal process, promoting long-term stewardship of natural resources and reduced environmental impact.
Handling Batteries and Power Sources
Batteries and other power sources within electronics present unique challenges due to their chemical composition and potential hazards. Lithium-ion, nickel-cadmium, and lead-acid batteries can pose fire, explosion, and contamination risks if punctured, overheated, or improperly disposed of. It is crucial to store these power sources separately from other e-waste and follow facility-specific disposal instructions. Using protective gloves, eye protection, and non-conductive containers adds an extra layer of safety during handling and storage.
Proper labeling of batteries and ensuring they are fully insulated prevents accidental short-circuits and chemical leaks. Many recycling centers offer dedicated battery collection programs, simplifying safe disposal while avoiding environmental contamination. In addition to safety, recycling batteries recovers valuable metals like cobalt, nickel, and lead, reducing the demand for virgin resources. By handling power sources carefully, individuals contribute to a safer disposal process while supporting sustainable practices and responsible resource management in the e-waste ecosystem.
Preventing Data Breaches When Disposing Electronics
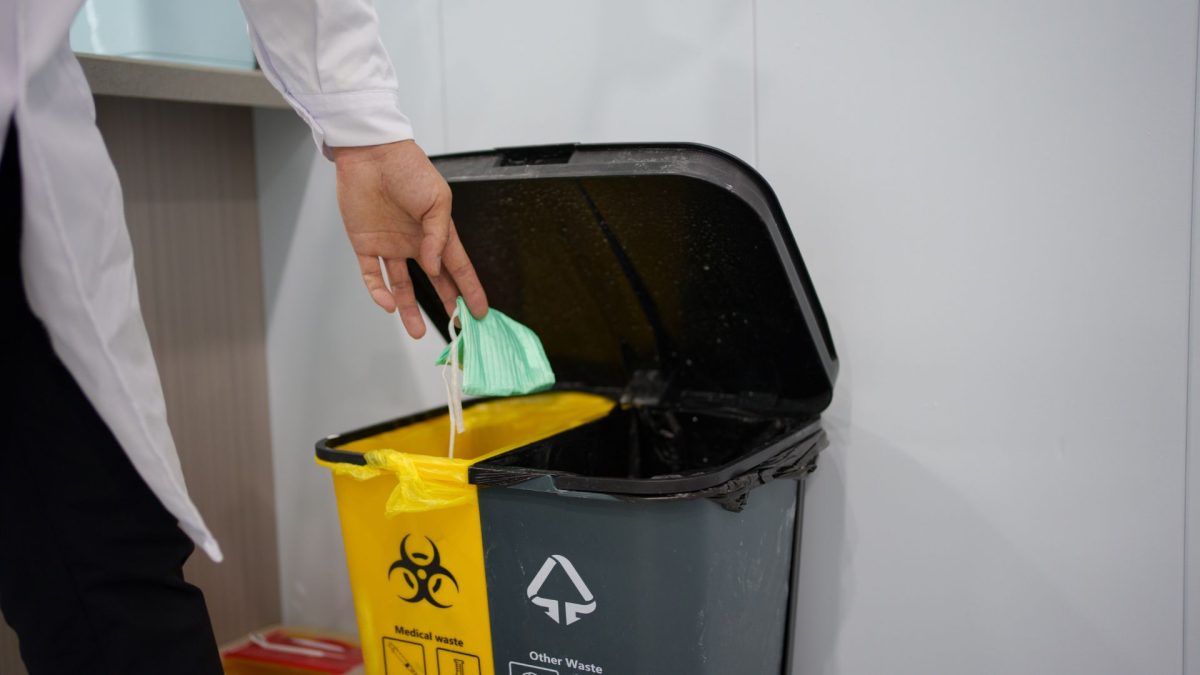
Disposing of electronics containing personal or sensitive information requires special consideration to prevent data breaches. Devices like computers, tablets, and smartphones often store passwords, financial data, and private communications. Secure data deletion, such as factory resets or certified data destruction services, is essential before disposal. Many e-waste recyclers offer guarantees that all data will be safely wiped, providing peace of mind while ensuring legal and privacy compliance.
Additionally, physically destroying storage media, such as hard drives or memory cards, further mitigates the risk of unauthorized access. Organizing electronics by device type and noting those with sensitive data helps ensure careful handling during the recycling process. Taking these precautions protects both personal information and the integrity of the disposal system, reinforcing the connection between safety, environmental responsibility, and digital security. Responsible data management complements the broader effort to safely recycle hazardous e-waste materials.
Community Participation in Hazardous E-Waste Collection
Community involvement strengthens hazardous e-waste collection efforts by providing accessible drop-off points and educational programs. Local governments, schools, and organizations often host collection events to safely gather electronics, offering residents an easy and environmentally friendly disposal option. Participating in these initiatives promotes environmental awareness and creates a culture of responsibility around e-waste management. These programs often collaborate with certified recyclers, ensuring hazardous materials are processed safely and sustainably.
Engaging with community collection events also encourages neighbors and peers to adopt similar practices, amplifying the positive impact. Outreach campaigns can inform residents about hazardous components, proper packaging, and the importance of separating e-waste from regular trash. By collectively addressing the challenges of hazardous e-waste, communities reduce environmental risks, prevent illegal dumping, and foster collaboration between citizens, local authorities, and professional recyclers. Participation strengthens the connection between responsible disposal habits and environmental stewardship at the local level.
Future-Proofing Your E-Waste Disposal Habits
Planning ahead ensures that hazardous e-waste is managed sustainably over the long term. Establishing a regular schedule for evaluating and disposing of outdated electronics prevents accumulation and reduces last-minute disposal risks. Staying informed about technological advances, new recycling techniques, and updated regulations helps individuals adapt their disposal habits effectively. By anticipating changes, you can make environmentally sound choices consistently, minimizing both health hazards and ecological impact.
Additionally, investing in durable, recyclable electronics and responsibly sourcing new devices can reduce the volume of hazardous e-waste produced. Educating family members or colleagues on proper disposal practices further strengthens sustainable habits, creating a culture of accountability and mindfulness. Future-proofing disposal habits fosters a proactive approach to e-waste management, ensuring that each generation contributes to safer, greener communities while reducing the long-term burden on recycling infrastructure and the environment.
Conclusion
Safely disposing of hazardous e-waste is a responsibility that combines awareness, preparation, and engagement with professional services. By understanding the risks, identifying dangerous components, and leveraging certified recycling facilities, individuals can prevent environmental contamination and protect public health. Proper preparation, careful transportation, and secure data handling enhance safety and ensure compliance with local regulations, creating a responsible e-waste ecosystem. Participating in community initiatives and maintaining long-term disposal habits further reinforces the importance of sustainable practices.
For residents of Palatine, IL seeking expert assistance, 24-7 Junk Removal provides comprehensive junk removal services including the safe disposal of hazardous e-waste. Their professional teams handle materials efficiently, ensuring environmentally responsible recycling and data protection. Contact 24-7 Junk Removal at (773) 309-6966 or visit their location at 611 W. Wise Schaumburg, IL 60193 for reliable junk removal solutions. Their commitment to sustainable practices makes them a trusted partner for safeguarding both your property and the environment, offering peace of mind with every service.